Copy the highlighted text or selected item.
.
Undo any change. For example, if you cut
text, pressing this will undo it. This can also often be pressed
multiple times to undo multiple changes. Pressing Ctrl + Y would re-do
the undo.
Open the Find in any program. This includes
your Internet browser to find text on the current page.
Quickly switch between open programs.
Open help for the program you're in.
Print what's currently being viewed in
programs such as Microsoft Word or your Internet browser.
Move the cursor one word at a time instead
of one character at a time. If you wanted to highlight one word at a
time you can hold down Ctrl + Alt and then press the left or right
arrow key to move one word at a time in that direction while
highlighting each word.
Move the cursor to the beginning or end of a document.
in that direction. When browsing
the Internet pressing the space bar will also move the page down one
page at a time.
The Desktop is the main background on your screen when you are working
on your PC. It consists of a background picture or 'wallpaper', any program
shortcuts you have created, and the Taskbar.
The Taskbar runs along the bottom of the screen (or the side, or top - you
can click and drag it wherever you want to place it) and shows the date and time
as well as giving you access to the Start menu. You can also put program
shortcuts on the taskbar so that one click will activate a particular
program.
Left-clicking on the Start menu brings up the All Programs list
of shortcuts to programs you have on your computer. These are often arranged in
'folders', so that you can find all the programs made by one company under a
folder in their name.
By holding the mouse pointer over a folder you will see a new list appear of
whatever programs are within that folder. Some programs will have several
related entries - so you might see a README (a document that has instructions
for using the program), or an option to Uninstall (remove the program
from your PC).
You can access your Desktop settings by right-clicking anywhere on the
background wallpaper and then clicking on Properties
Windows
The operating system that runs all your programs and allows you to easily
interact with your PC is called Windows for a good reason. It allows you
to work with several different items and programs at once, all in their own
'window'. A window is like a smaller screen contained within a box on your main
screen.
When you are working with a window it is brought to the 'front' of the
screen, overlapping the Desktop and any other items behind it, so that you can
focus on whatever is in the window.
In this way, you can have several windows open at the same time containing
different programs that can be opened, closed, and re-arranged across the
screen. This means you can do multiple tasks at the same time, such as playing
your favorite music while writing an e-mail for example.
Files And Folders
Every item stored on your PC, whether it is a document, picture, song, game
or whatever, is a file. A file can only be activated by programs that
understand and are able to use it.
For example, you cannot use a music program to open a letter document. Each
program on your computer understands what type of file it can or cannot use by
the fact that every file has a filetype given to it.
This takes the form of a few extra letters or numbers added on to its name
after a full stop. So for example, 'myletter.doc' is a file named 'myletter'
with the filetype '.doc', meaning it will require a program that understands doc
(document) files, such as Microsoft Word.
There are many different filetypes. Read Common Filetypes for a list of the more
common.
Any one single program or application can actually consist of many different
files, all working together to achieve the same task.
This means modern computers can have millions of files spread across
different locations. Folders help organize these files, so that for each
particular program there can be one folder that contains all the files it needs
in one place.
A folder can even contain other folders inside it called 'sub-folders'. For
example, to organize your holiday pictures together you might have a folder
called 'Holidays 2006' and then other sub-folders within that for each
particular holiday destination, for example 'France 2006'.
You can create your own folders. You can also create shortcuts to make it
easier to find particular files. Read Organize Your
Files/Folders/Shortcuts to learn more.
You can take a look at an example of a folder now. On your Desktop you should
see a shortcut icon called My Documents. Double-clicking this will open a
new window showing the contents of the My Documents folder.
My Documents
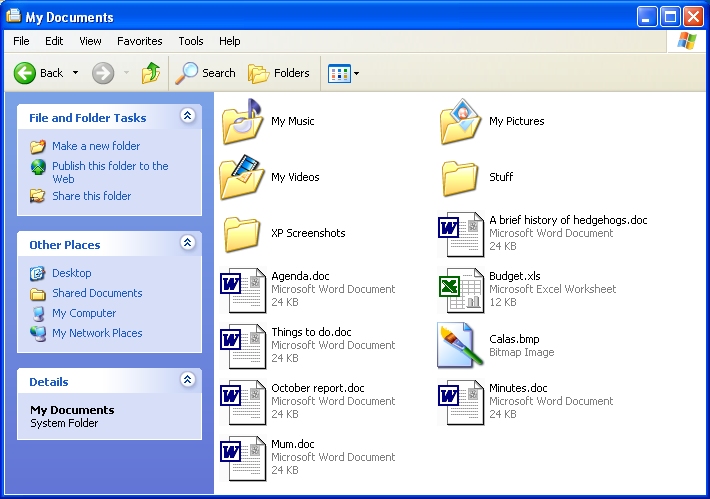
My Documents is a folder on your computer that is automatically created for
you, so that you can store all your own files in one place away from all the
program and system folders, making them easier to find.
Double-click the My Documents shortcut on the Desktop and you will see
a list of folders, within which are your files. To see what is inside a folder,
double-click on it and the current window will change to show the contents.
You may see some other folders which have been automatically created for you
to help you store certain types of files, such as My Music, My
Pictures and My Videos. However, you do not have to use these, and
you can store any of your files in any folder you want to. You don't even have
to use My Documents, though it is usually easier if you do.
My Computer
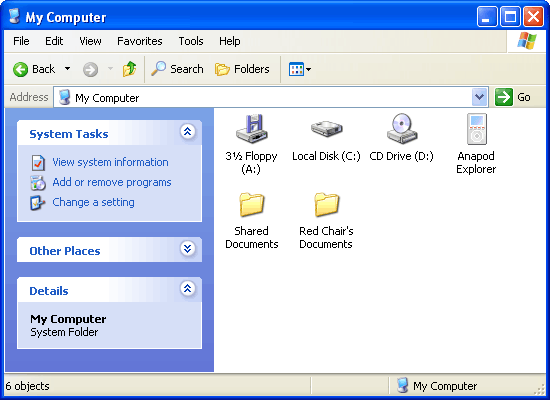
Close any open windows by clicking the X button in the top-right. On
your Desktop, double-click the My Computer shortcut and you will see a
list of locations where files are stored on your PC's disk drives.
If you double-click the Local Disk
(your Hard Disk, usually C: ) you can
see all the folders that are stored on your Hard Disk - this will be the part of
your PC where all your files are usually kept, unless you have extra disk
drives.
The Program Files and
Windows folders here are especially important, and should usually not be
changed as they contain the files necessary for programs and Windows to run.
All files take up 'disk space' and your
computer only has so much room to store them all. If you want to see how much of
your Hard Disk you have used up so far, and how much space you have left,
double-click My Computer again and this time, instead of double-clicking
the Local Disk, right-click it and select Properties.
If you find you are running out of disk space, you should try to clean up some unnecessary files. Read Clean Out And Clean Up Files for
more information.
If you decide you need a lot more space than you have, it is possible to buy
extra Hard Drives and connect them to your computer.
If you right-click the My Computer icon on the Desktop rather than
double-clicking it, and then click on Properties, you can see detailed
information about your PC including your hardware devices and performance
setting
The Control Panel
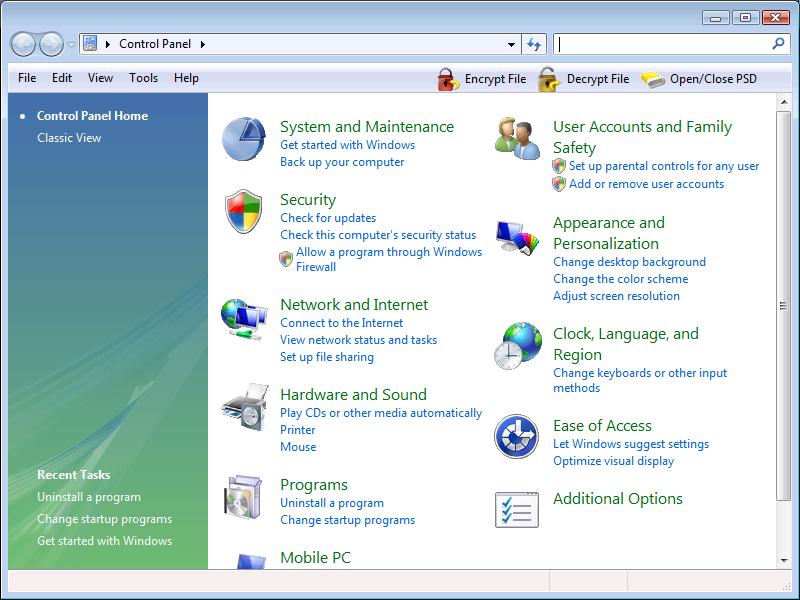
The Control Panel is a collection of all the important options you
will need when you want to change settings on your computer. You can find
control icons for display, sound, Internet, hardware, programs, security and
system settings. To access the Control Panel, click the Start menu and
then click Control Panel.
Changing settings in the Control Panel can make big changes to your PC's
setup. For example, the Appearance and Themes or Display options
in the Control Panel can affect the quality of your screen and the size of text.
Read Change Display
Settings And Text Size for more information.
Click on your Start menu and then Help and Support for more
help with using your PC and particular Windows features.




 1
1




 1
1